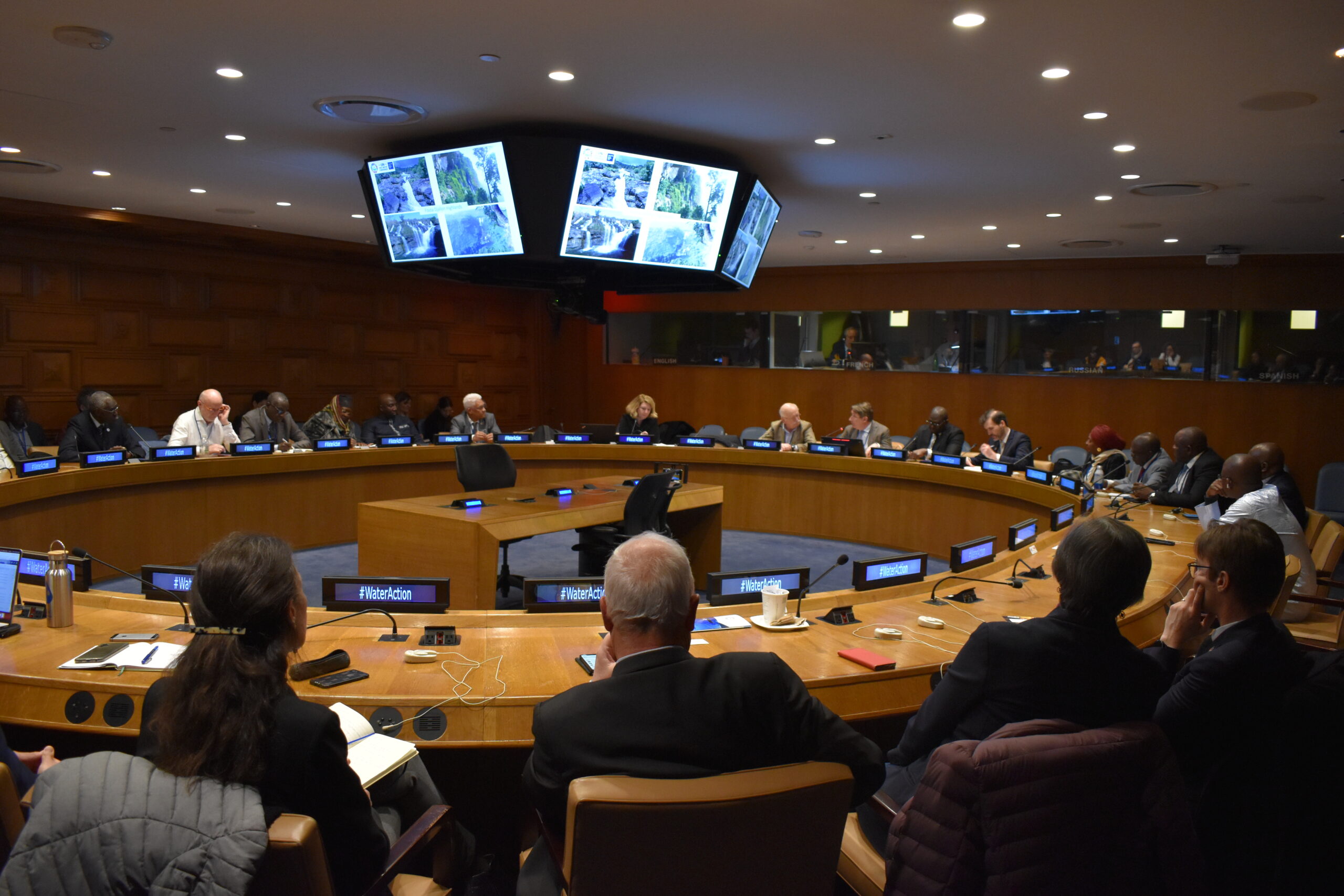
River basin organizations at the heart of preservation efforts
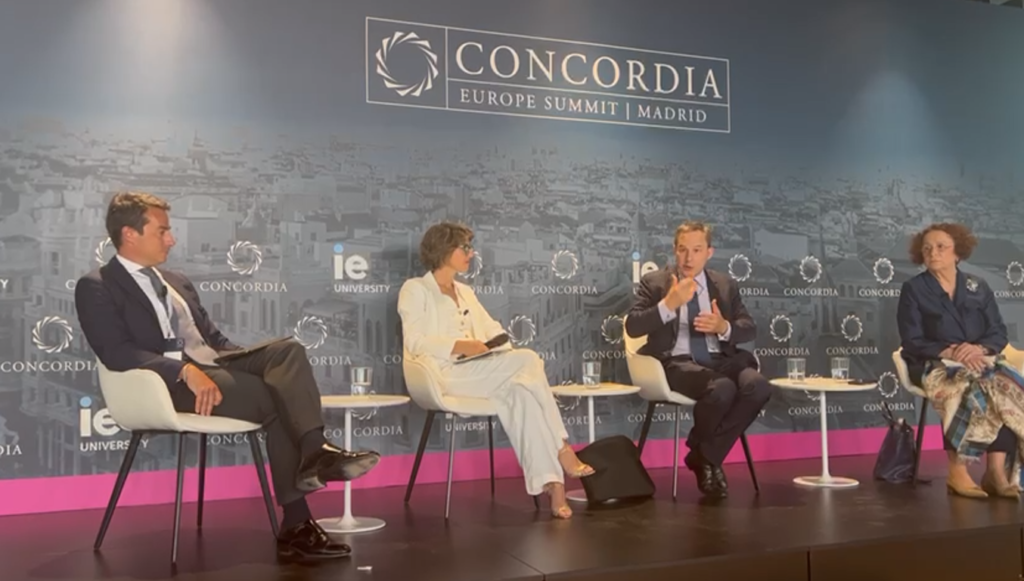
Lionel Goujon, Head of the Water and Sanitation Division of the French Development Agency (AFD) presented the existing preservation and sustainable management initiatives as well as the actions already carried out in the field by the AFD. These have been developed and carried out in partnership with the various basin organizations of the region. The presence of senior officials of these basin organizations, with Mr. Soufiana Dabo for the OMVS, an organization that AFD has been supporting for about 40 years, and Mr. Abderahim Bireme Hamid for the NBA, with which AFD has been collaborating for about 20 years, illustrated the investment and the central role of these organizations in the management of water resources and the preservation of the region’s ecosystems.
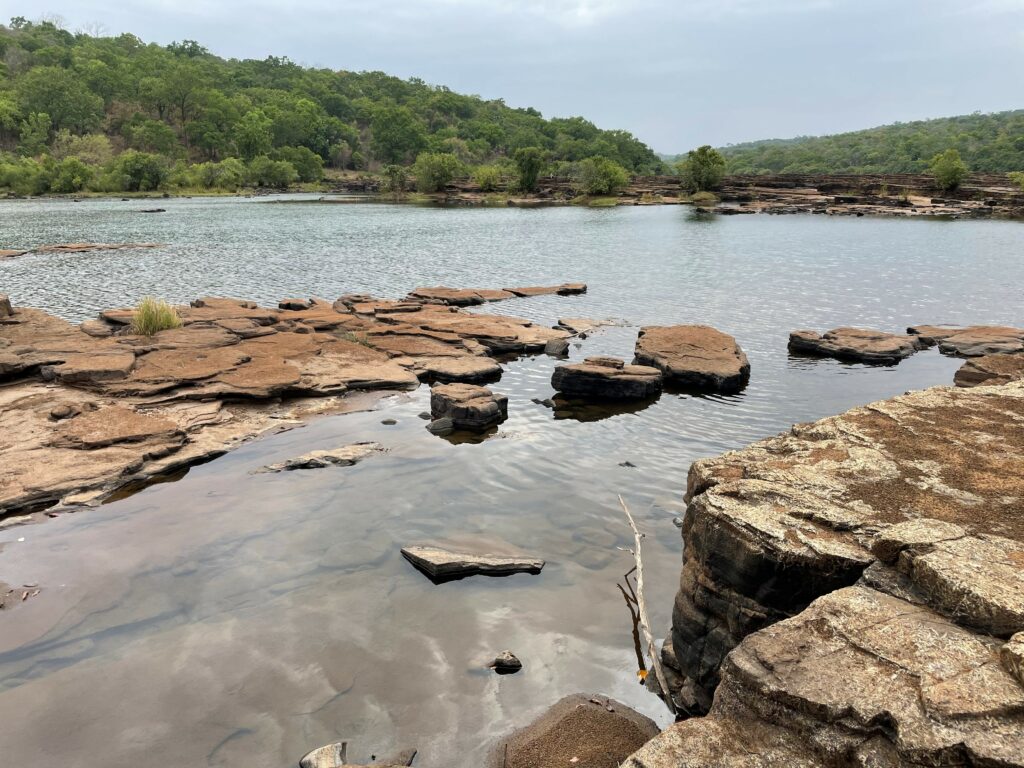
It is about avoiding the tragedy of the commons and the unfolding tragedy of Fouta Djallon, Mr. Goujon stated, referencing Elinor Ostrom, Nobel Prize in Economics in 2009. The challenges in the conservation efforts are numerous: lack of knowledge about the declining resource and its ecosystem, lack of measurements, and lack of data on the consequences of ongoing hydrological changes, as well as the need for new technologies and human resources and devices to maintain measurement networks.
AFD’s action in partnership with basin organizations is structured around projects such as the SCREEN project with OMVS, a project of altimetric measurements with satellite technologies in collaboration with French actors like CNR, IRD, BRL, and CNES. The DYNOBA project for the revitalization of transboundary basin organizations in Africa encourages the sharing of experiences between basin organizations. The Fouta Djallon could be a field of application of this exchange. AFD is also currently working on a project to support Guinea’s national meteorological services to strengthen national meteorology and produce more reliable data.
“There are several levels to work on: institutional, international, national, and local with the populations in order to have a beneficial impact on this region,” Mr. Goujon concluded.
An action plan for the Fouta Djallon
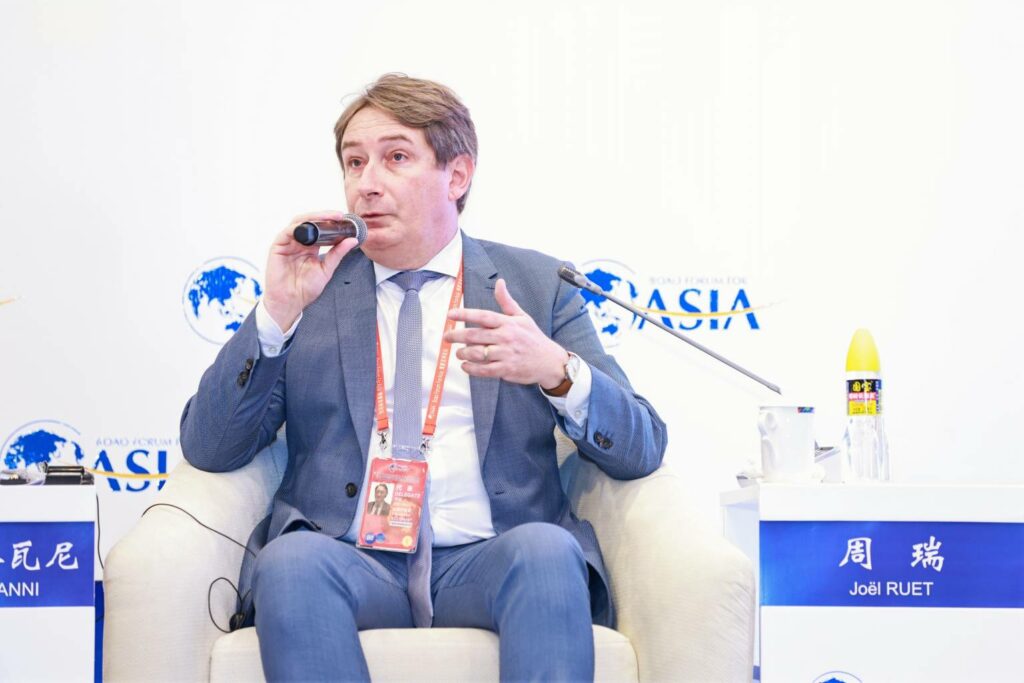
The objective of this side event was not only to alert the international community on the alarming situation of a dying Fouta Djallon but also to present an action plan and the key avenues of action for the preservation of the highlands. Joel Ruet, President, The Bridge Tank & economist at the Interdisciplinary Institute of Innovation i3t, CNRS presented some essential features of such an action plan.
- Supporting and mobilizing local communities by establishing a catalogue and an academy of durable best practices, combining both traditional and modern agricultural and ecosystem preservation methods, e.g. resilient agroforestry, to raise awareness and train local populations;
- Fostering local and regional research and innovation to increase knowledge and data of the Fouta Djallon’s resources and ecosystems. This will be achieved by establishing and supporting incubators of technological startups, supporting academic research projects, local environmental engineering, and the development of nature-based solutions;
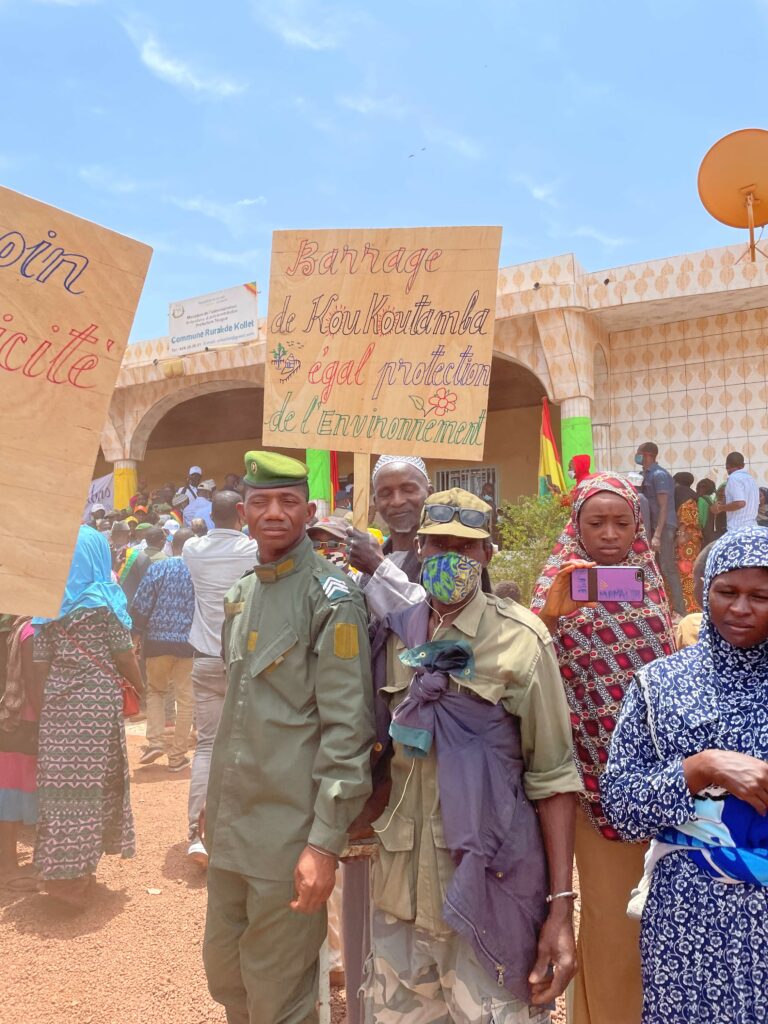
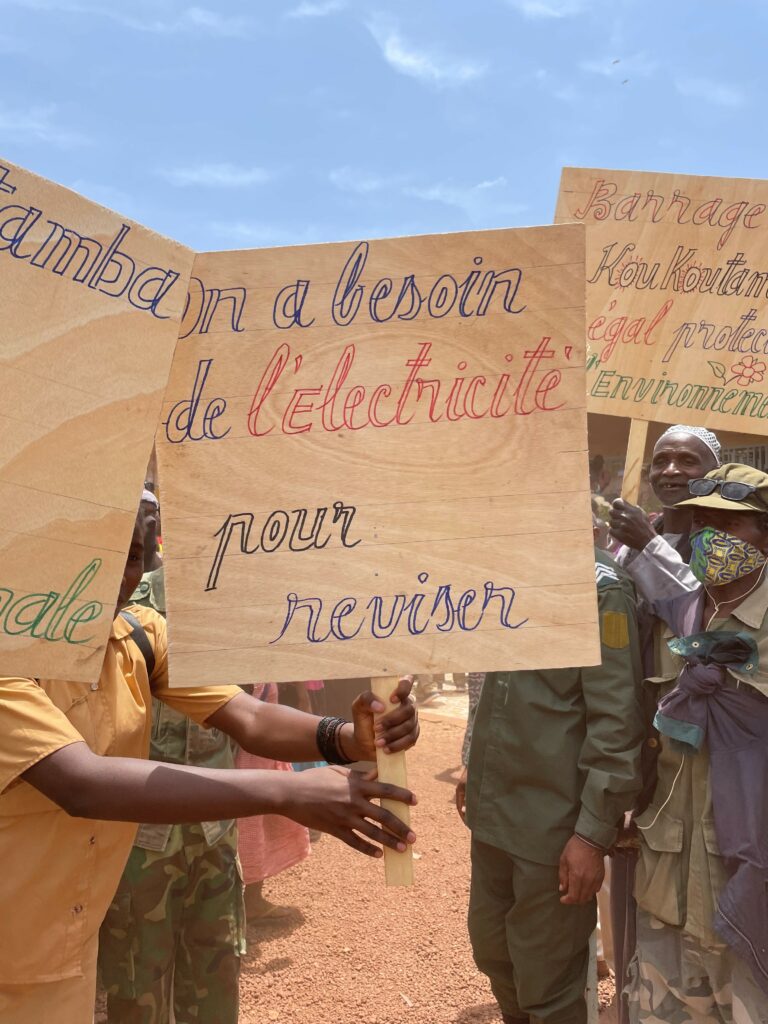
- Fostering political will and regional cooperation by creating an assembly of West African states, RBOs, and multilateral organizations, backed by the international community, for the Fouta Djallon to develop a regional cooperation framework around this common resource and ensure social, societal, and environmental sustainability in the highlands and across the region;
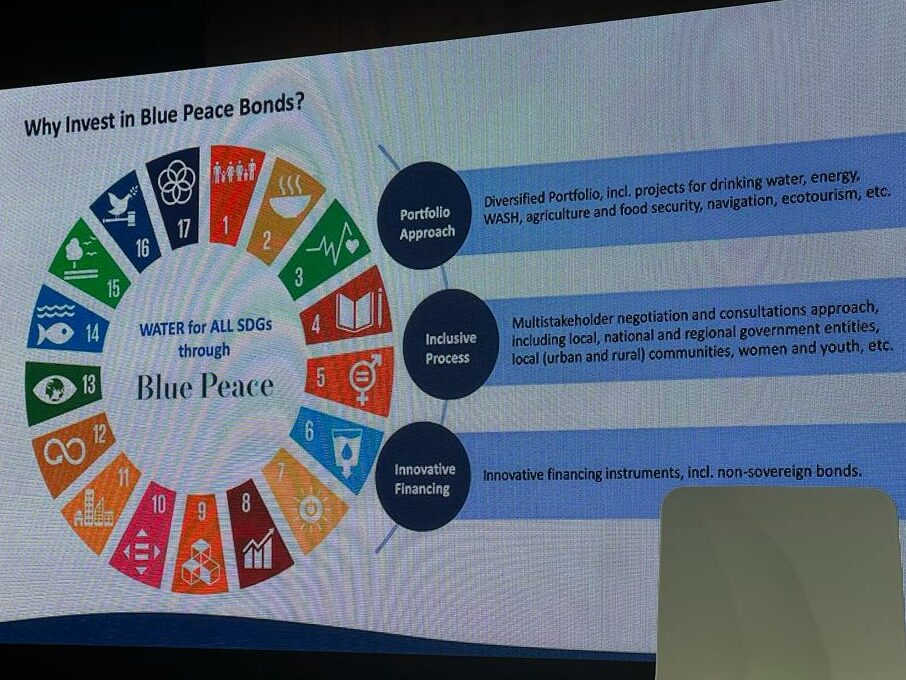
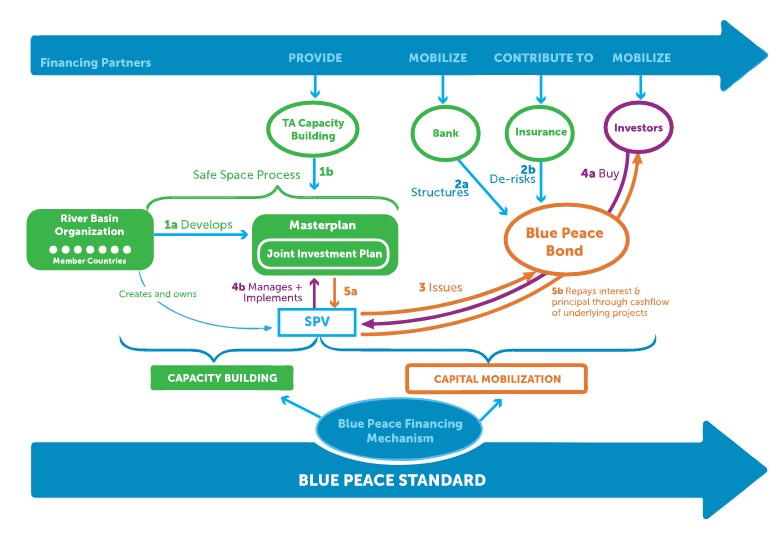
- Mobilising new green finance mechanisms in support of the Fouta Djallon by establishing a green-blue bond dedicated for the preservation of biodiversity and the development of the highlands with international support.
In the continuity of the actions already implemented, concerted action across the sub-region to preserve the Fouta Djallon will have to involve basin organizations. The issue of governance was also highlighted by Lionel Goujon, who advocated for a governance at different levels, involving basin organizations, states and sub-regional economic communities. “There is a need to create coalitions and cooperation platforms today,” Joël Ruet stressed, which will necessarily involve local communities, in order to determine which traditional methods need to evolve and what traditional knowledge can be mobilized as more sustainable and resilient farming or agroforestry methods. According to Soufiana Dabo, the priority is to adapt and rethink existing solutions.
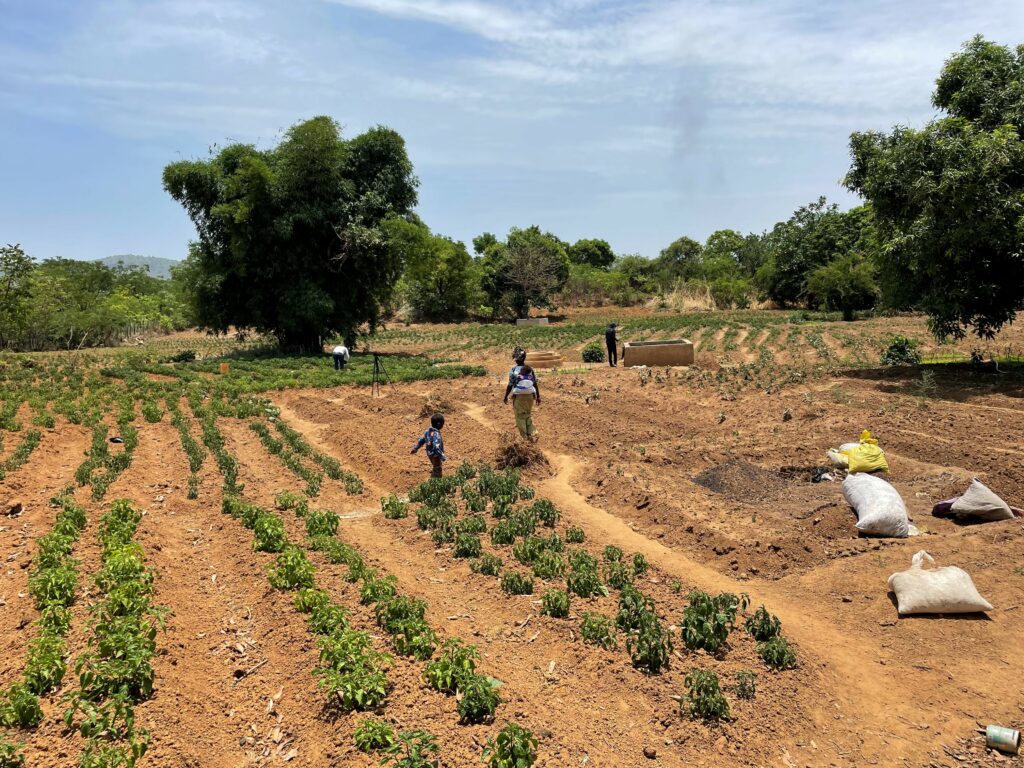
A tool which will play an important role in this process is the Fouta Djallon Observatory set up by the OMVS. According to Mr. Dabo, it will allow to observe, analyze and act in the Fouta Djallon. Soufiana Dabo took the opportunity to call for support of the Observatory as a center of research, reflection and data collection necessary for the evolution of the highlands. This evolution aims at accompanying the communities in their transition, either towards other activities that will have less impact on the ecosystem of the highlands, or to modernize current practices and activities undertaken by local populations. Within the framework of its IWRM programs, OMVS has launched the first initiatives in this direction, including agricultural development projects and the establishment of irrigated and fenced areas to settle the population. The rehabilitation of fish reserves hopes to turn fishing into an alternative source of income.
“We must not oppose socio-economic and human development to nature and the environment,” Joël Ruet insisted.
Finally, a last community that needs to be mobilized are the young graduates of the region’s universities. Mr. Ruet emphasized the importance of local technological entrepreneurship. The support of incubators of young local entrepreneurs returning to the field after their studies would provide the human resources to sustain the measurement and data collection systems necessary for all preservation efforts. This data can also be mobilized for sustainable finance mechanisms that enable, according to Mr. Ruet, “transformational changes going to scale.”
This session is part of The Bridge Tank’s long-standing commitment to the preservation of the Fouta Djallon. At the World Water Forum in Dakar in March 2022, The Bridge Tank and IFGR had already co-organized a session on the issue of safeguarding the Fouta Djalon highlands, in partnership with OMVS and Organisation pour la Mise en Valeur du Fleuve Gambie (OMVG). Previously, Joel Ruet, President, The Bridge Tank, had also participated in a field mission in the Fouta Djalon led by our board member Hamed Semega, then High Commissioner of OMVS.